Employment Intensity and Rise of Part-Time Work
Why part-time?
While the headline unemployment rate stands at 4.1%, a deeper analysis of employment intensity—the average number of hours worked per week—shows a shift in the labor market.
Understanding Employment Intensity
Employment intensity measures the average number of hours employees work per week, serving as a crucial indicator of labor market health and economic trends. This metric provides a deeper look beyond what traditional employment statistics might miss, particularly during economic transition.
Current Landscape
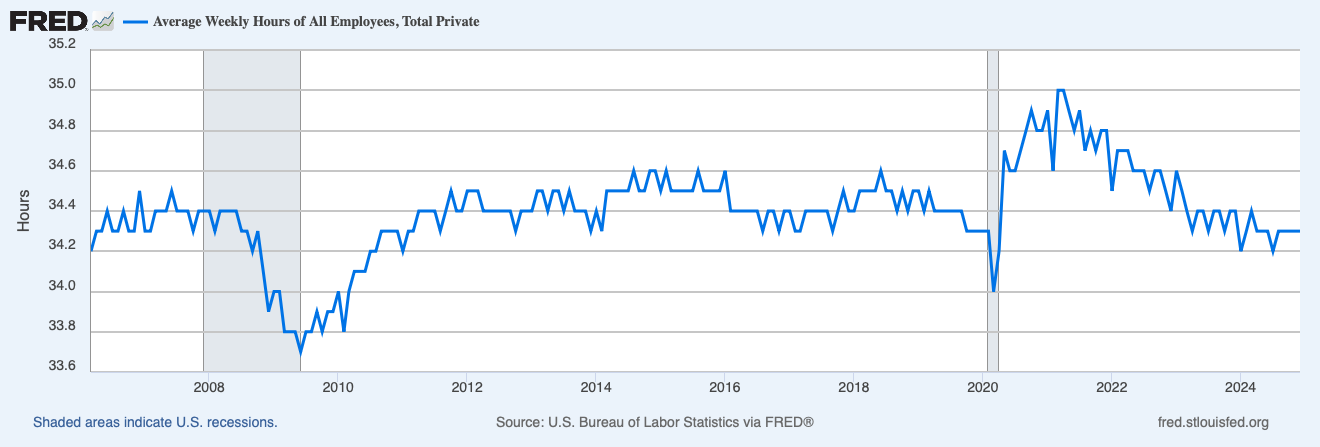
The average workweek has contracted to 34.3 hours, representing a decline of approximately 45 minutes from its 2021 peak. This reduction signals a fundamental shift in both employer strategies and workforce preferences.
Historical Context and Market Evolution
The labor market's transformation since 2021 tells a compelling story:
Peak Intensity (2021)
During labor shortages of 2021, employers pushed weekly hours to historic highs of 35 hours, maximizing output from their existing workforce amid fierce competition for talent.
Current Market Dynamics
Today's landscape reflects a strategic pivot. Rather than implementing layoffs, employers are maintaining their workforce while adjusting hours downward—a more nuanced approach to managing labor costs and operational efficiency. They are keeping their employees so that they do not struggle with labor shortages again. Hiring is costly, and maintaining some slack at the firm helps.
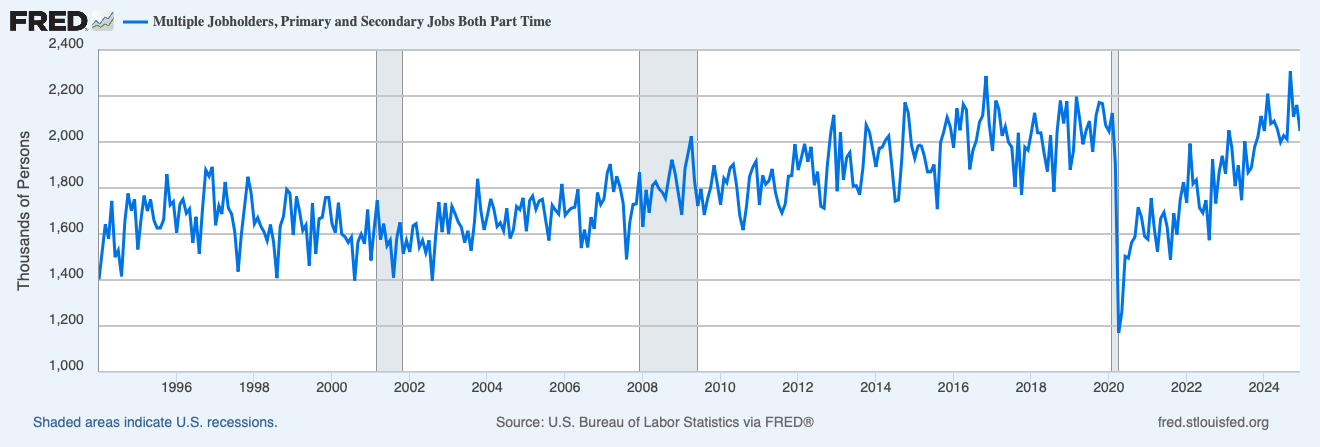
The Rise of Multiple Job Holders
A striking trend emerges in the multiple-job holder statistics. Eight million Americans currently hold multiple jobs, the highest number since 1994. Of these, two million individuals combine multiple part-time positions. It is unclear if this increase is due to employee preferences for more flexible work, economic and noneconomic conditions that might prevent the employee from working, or an employer-driven change in the availability of full-time work.
Why Part-Time Employment?
The increase in part-time employment requires careful analysis:
Some workers actively choose reduced hours to achieve better work-life balance
Others may accept part-time positions due to economic constraints or family responsibilities
The distinction between voluntary and involuntary part-time work remains crucial for understanding labor market health
Compensation Evolution
The changing landscape necessitates a fresh examination of wage growth patterns across different employment categories and how benefits are distributed between part-time and full-time workers,
Market Adaptability
Employers show increased willingness to retain talent through hours reduction. While workers demonstrate greater flexibility in combining multiple positions
The Takeaway
The decline in employment intensity and increased availability of part-time work represent more than a temporary adjustment—they potentially signal a structural transformation in American labor markets.